Master data management
Breaking down the data jargon: How MDM and ADM fit into your data expansion strategy

In 28 February 2025
In a world where data drives digital transformation, it is essential to structure its management effectively. This is where Master Data Management (MDM) and Application Data Management (ADM) come into play. These two complementary disciplines play a central role in ensuring data consistency, reliability, and efficient utilization.
MDM and ADM: Understanding the Difference
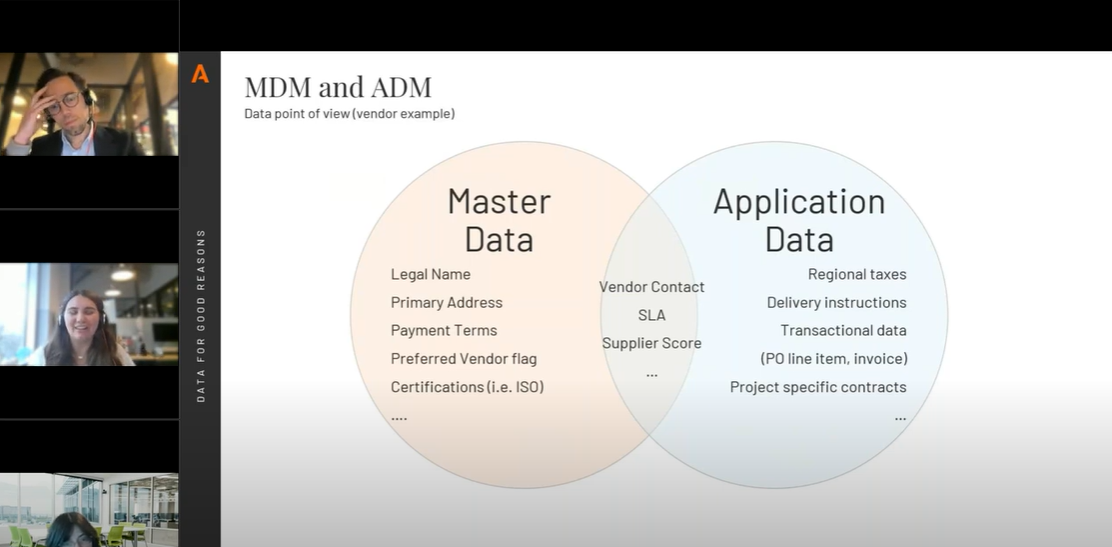
Master Data Management (MDM) aims to centralize, harmonize, and govern an organization’s master data, such as customer, product, supplier, or site information. It ensures a single source of truth, enabling informed strategic decision-making.
On the other hand, Application Data Management (ADM) focuses on managing data specific to a particular application (ERP, CRM, etc.), often leveraging extracts of master data. The goal is to optimize data usage within a given system without impacting the entire organization.
Complementarity and Transition to Unified Enterprise Data Management
Contrary to common misconceptions, ADM does not replace MDM. Instead, they work together to facilitate the transition from an application-centric model to an enterprise-centric one.
While ERPs and CRMs rely on ADM to manage data specific to their operations, MDM acts as a transversal layer that ensures data consistency and integrity across the entire information system. This results in better integration, process simplification, and enhanced agility to adapt to evolving IT landscapes.
Defining Where and How to Manage Data
One of the biggest challenges in data management is determining where a given piece of data should be managed. Some data clearly belongs to master data (e.g., a supplier’s legal address), while other data is application-specific (e.g., a supplier evaluation note used only in a sourcing application).
When the distinction is unclear, it is crucial to evaluate:
- How the data is used (is it utilized across multiple departments or only within a single application?)
- The stakeholders involved (who is responsible for it?)
- The organizational framework and related processes
By applying a “shaping” phase upfront, organizations can anticipate these questions, prevent inconsistencies, and better align data management with business needs. Moreover, “Shaping” is a process that helps defining objectives, identifying potential challenges, and structuring data before implementation to ensure a smoother and more effective execution.
Overcoming Organizational Challenges
Deploying a data management strategy is not just a technological project. It is, above all, a human and organizational challenge, with several key hurdles:
- Resistance to change and internal politics: Engaging stakeholderssuch as leadership, peers and end users from the outset is crucial to ensuring buy-in.
- Poorly defined scope: Attempting to centralize everything within a single system can lead to an overly complex and difficult-to-maintain environment.
- Change fatigue: In the context of transformation (mergers, ERP migration, etc.), it is essential to avoid overload and prioritize key steps.
Creating Value with a Balanced Approach
For MDM and ADM to deliver real value, they must be integrated into a global strategy aligned with business objectives. This involves:
- Clear and business-friendly communication, avoiding technical jargon
- Proactive change management, involving all stakeholders
- An iterative approach, fostering quick and measurable gains
By structuring your data management effectively, you create a solid foundation for optimized decision-making, greater agility, and improved compliance with regulatory requirements.
MDM and ADM are essential pillars for effectively structuring data management within an organization. By understanding their differences and complementarity, businesses can ensure data consistency, reliability, and optimal utilization. However, their implementation goes beyond a purely technological approach—it requires strategic planning, clear governance, and effective change management. By adopting a balanced and iterative approach, organizations can turn data management into a true driver of performance and innovation.
At Apgar, we help businesses navigate these complexities by providing expert guidance, tailored methodologies, and proven frameworks to ensure a seamless and value-driven data transformation.

Webinar
Breaking Down the Data Jargon: How MDM and ADM Fit into Your Data Expansion Strategy
Would you like to get in touch with our experts?
If you agree, disagree or have something to add to these views on corporate strategy, please contact us.